After nearly five years of planning, the Kenya Tradenet System, the electronic platform for lodging trade documents and making payments becomes fully operational tomorrow, July 1st.
The system is set to facilitate international trade by reducing delays and transaction costs related to processing of imports and exports documentation. It is expected to boost transparency in cargo clearance, and at the same time improve revenue collection. KenTrade, an agency formed in 2011 to implement the system, says cross-border trade is headed for a radical shift.
Sandra Chao-Blasto talked to KenTrade acting chief executive Amos Wangora on uptake of the electronic system and its benefits.
What will traders be doing differently once the electronic single window system becomes fully operational?
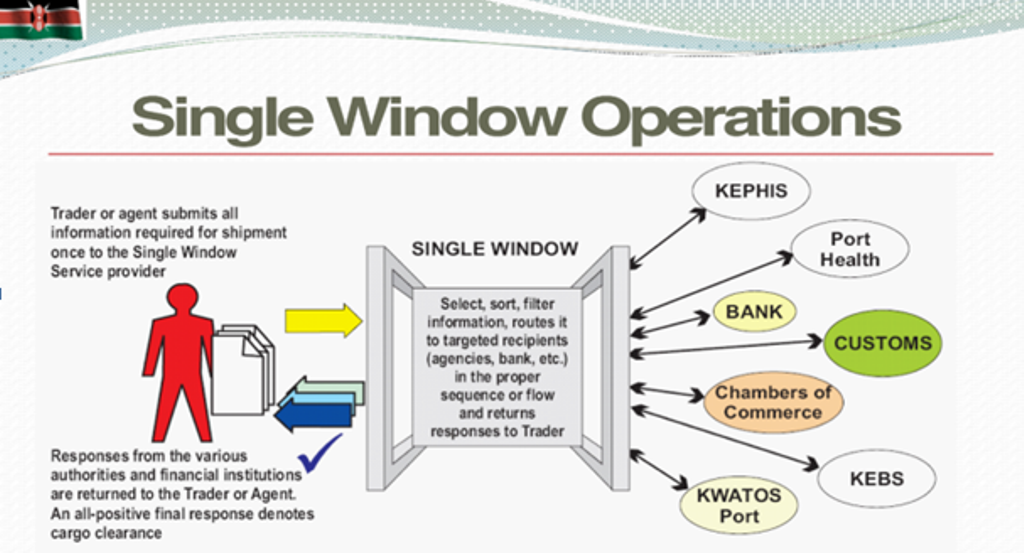
There will be a complete crossover from the manual to an electronic platform on July 1st. Traders will submit all cargo clearance-related documents electronically, make electronic payments and receive approved documents online.
Which are these documents accessible through the Kenya Tradenet?
Nearly all the necessary documents, including Unique Consignment Reference (UCR), Impending Arrival Report (IAR), Bay Plan (BAPLIE), Manifest Sea, Air Manifest, Manifest Road, Import Declaration Form (IDF) and Dynamic Risk Management. Others are security bonds, exemptions, payments records, availability of attachments, cargo release dash board, and reports.
Which government agencies have been linked so far to the electronic platform?
Basically all the agencies that handle import and export permits are on board. They include Pharmacy and Poisons Board, Port Health, Kenya Revenue Authority, Kenya Bureau of Standards, Kephis, AFFA directorates, veterinary department, Kenya Dairy Board and the Radiation Protection Board. We have also connected Pest Control and Produce Board, Kenya Wildlife Services, National Biosafety Authority, Central Firearms Bureau, Nursing Council of Kenya, National Environment Management Authority and Kenya Medical Laboratory Technicians and Technologists Board.
Will the electronic system edge out clearing and forwarding agents in cross-border trade?
No, and we don’t expect any job losses. The system will instead enable the cargo agents to do their work efficiently. An improved business environment is expected to lead to reduced costs of doing business and increased efficiency in trade.
What are the alternatives once you discard the manual system?
Adequate redundancies have been provided to ensure uptime for the system with increased transaction load. Our highly skilled and experienced technology implementation partner (CrimsonLogic) was also instrumental in adequately sizing the infrastructure to ensure that the system does not crash with heavy transaction loads.
Additionally, the system’s performance has been tested and the system has been in use for over one year and has handled increasing load gracefully.
What guarantee can you give traders that hackers will not interfere with the system and gain access to confidential information?
As per ICT security best practice used to secure key national information systems, KenTrade has implemented a host of cutting-edge information security technologies to provide assurance of system security. We also have a highly qualified ICT team that works to ensure information security.
What are some of the benefits the system has generated for the government so far?
It has brought greater harmonisation and better sharing of data across government departments and agencies, resulting in improved efficiency, transparency and effectiveness of official controls. This has enhanced revenue collection and reduced cost of doing business both for the government and the business community.
In terms of revenue collection, how efficient has the system been?
The system has integrated with KRA’s i-Tax system to facilitate faster and efficient electronic payments for applications.
Banks initially appeared averse to the system. Which banks do you have on board to enable traders make regulatory payments?
Initially a number of banks experienced teething problems in configuring their systems to be able to process e-slips generated through Kenya Tradenet system.
This has since been resolved and so far we have National Bank, Equity, I&M, Co-operative Bank, KCB, Standard Chartered, Citi, Bank of Africa. The rest of the banks are piloting the system.